41 dosage calculations with labels
Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 2: On the right side, place the information given with the same label needed in the numerator. In this example, we know that the drug concentration available is 0.25 mg/mL. Place mL in the numerator and 0.25 mg in the denominator. Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into ... PDF Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet - NursingSOS Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet LEGAL DISCLAIMER: This cheat sheet is intended for educational purposes only. This is not medical advice and errors may occur. Never treat a patient or make a nursing or medical decision based solely on the information provided in this video. Never practice nursing or medicine unless you have a proper license to ...
Dosage and Calculations - Registered Nurse RN Some types of dosage calculations require you to determine the dosage of a medication or the amount to be administered based on the prescribing provider's order and the patient's weight. These types of drug problems require converting pounds to kilograms and that you apply that […] Tablets and Capsules Dosage Calculations (Desired over Have Method)
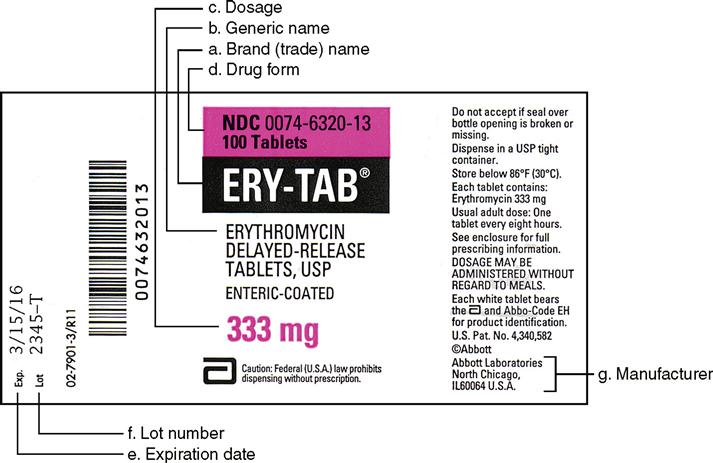
Dosage calculations with labels
Calculating from the labels | Learning Lab This short video is the second of three videos in the Nursing calculations - Finding the volume required section. It explains how to calculate medication dosage from labels using the method of mental calculation and proportinality to get the right dosage for drugs in solution. Nursing calculations: Calculating from the labels Watch on Transcript Oral Drug Dosage Calculator - Liquid Solution Syrup ×5 milliliter X (amount) =10 milliliter Description: This calculator determines the volume of liquid, solution or syrup to be administered to the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine. The concentration is the mass of medicine contained in a volume of liquid. The mass is the have dose. Dosage Calculator - [100% Free] - Calculators.io Here are the steps to follow for using this drug dosage calculator: First, enter the value of your Weight and choose the unit of measurement from the drop-down menu. Then enter the value of the Dosage and choose the unit of measurement from the drop-down menu. For liquid medications, also enter the value of the Medicine Concentration and choose ...
Dosage calculations with labels. RN Programs - Registered Nurse || RegisteredNursing.org For this oral dosage problem, you have to find out how many mL of tetracycline the patient will get when the doctor has ordered 150 mg and the syrup has 50 mg/ml. This problem is set up and calculated as shown below. 150 mg: x mL = 50 mg: 1 mL. 50 x = 150. X = 150/50 = 3 mL. Dosage (Drug) Calculations Nursing Review- COMPREHENSIVE This is a comprehensive dosage calculation review for nursing students. In this review we will start by working basic metric conversions and then progress to solving more complex dosage calculations. You will learn how to work the following drug calculation problems: Conversions. Oral Liquid Medications. Capsules and Tablets. Pharmacy Dosage Calculations - Pharmacy Tech Review First, note that both grams and milligrams are used in the problem so we need to do a measurement conversion. There are 1,000 milligrams per gram. The first ratio is one dose per 20mg so ¹⁄₂₀. The second ratio contains an unknown so initially it is ˣ⁄₁₀₀₀. Set these two ratios in a proportion. Dosage Proportion With Unknown. Dosage Calculation Using the Formula Method - Basicmedical Key H = The dosage strength available, what is on hand, or the weight of the medication on the label, including the unit of measurement. Examples: mg, g, etc. Q = The quantity or the unit of measure that contains the dosage that is available, in other words, the number of tablets, capsules, milliliters, etc. that contains the available dosage.
Dosage Calculations the Easy Way! - Straight A Nursing Everything except for tablets is crossed out, so we know we are ready to do some math. 1) Multiply across the top: 650 x 1. 2) Then divide across the bottom: ÷ 325. What answer did you get? Let's do one more easy one…. For this calculation, let's assume midazolam comes in 5 mg tablets. Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide + Quiz | KnowledgeDose The available stock is 2000 units/ml. The pharmacist has asked the pre-registration pharmacist to also state how many mls of colecalciferol Mr X should take on the dispensing label. What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method A formula is used to calculate the dose of a drug, often utilized when converting different units of measurements such as pounds to kilograms or kilograms to grams. The dimensional analysis approach or the factor-label method can be used to provide an additional safety check with the other methods of calculation. PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration
Dose Calculation Desired Over Have Formula Method - StatPearls - NCBI ... 1 pint = 2 cups 12 inches = 1 foot 1 L = 1.057 qt 1 lb = 16 oz 1 tbsp = 3 tsp 60 minute = 1 hour 1 cc = 1 mL 2 pints = 1 qt 8 oz = 240 mL = 1 glass 1 tsp = 60 gtt 1 pt = 500 mL = 16 oz 1 oz = 30 mL 4 oz = 120 mL (Casey, 2018) Technique There are 3 primary methods for the calculation of medication dosages, as referenced above. Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels Dosage Calculations - Lecture notes 1 Drug Development and Ethical Considerations Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Pharmacogenetics Preview text Dosage Calculation: Reading Drug Labels Chapter 11 Tarleton State University NURS 3310 Dr. Mary B. Winton Reading Drug Labels a. Brand/trade name b. Generic name c. Formulation d. Dosage strength e. Dosage Calculation Practice_Reading Labels.pdf - Dosage... Calculations (12-14) answers. 12) Number of of emtricitabine tablet required. Ordered dose = 200 mg. Available dose = 100 mg/tab. Number of tab required = 200/100 = 2 tablets. 13) ml of drug required. Volume (ml) = Desired dose/Dose in hand *Quantity. Here Desired dose = 600 mg. Dose in hand = 400 mg. Quantity = 1 ml. As per above formula Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College ONLY TWO ATTEMPTS allowed to obtain 90% for eligibility for enrollment. This is a 40 item exam. 36/40 required for a 90% score. 75 minutes will be allowed for test completion. Calculation problems will be fill-in-the-blank, NOT multiple choice. If you need testing accommodations contact Student Disability Services at 256-306-2630.

3. INTERPRETATION OF DRUG LABELS, DRUG ORDERS, BAR CODES, MAR AND eMAR, AUTOMATION OF MEDICATION ...
PDF Study Guide with Sample Questions Dosage Calculation Competency • The dosage calculation competency test is given as a proctored assessment in the college's Testing Center, located in the Library in Martin Hall. ... The label on the I.V. bag reads: Heparin 10,000 units in 500 mL D 5 W. How many mL/hr will deliver the correct dose? 13._Administer Heparin 1,000 units/hr from an l.V. bag mixed 40,000 units ...
Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and Reconstituted ... 400 mg = 1 ml (from the reconstitution directions on the label) You do not use the 1.8 ml of diluent added in your calculations, but you need this information to find the 400 mg per ml after reconstitution from the drug label. Equation for the dose in ml: Please notice: One day = 24 hours. Every 8 hours = 3 doses per day

Post a Comment for "41 dosage calculations with labels"